|
|
| Silanes & Silicones for Adhesives & Sealants |
SiSiB® SILANES & SILICONES are widely used in adhesives and sealants to improve environmental resistance, increase adhesion and other mechanical properties, provide a secondary moisture-activated curing mechanism, filler modification, surface priming, end-capping strategies, water scavenging, formulation stability, adhesion catalysis, etc.
|
 |
Silane as Adhesion Promoter |
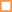
SiSiB® silane adhesion promoters are bifunctional organosilicone compounds which act as molecular bridges between the polymer matrix of an adhesive or sealant and the substrate, either inorganic or organic. SiSiB® SILANES can improve adhesive or sealant adhesion significantly. SiSiB® SILANES react chemically and promote adhesion: (1) between the base polymer in a sealant and the inorganic fillers in the formulation and / or (2) between the base polymer and the substrate.
|
|
 |
The silane end contains hydrolysable alkoxy groups that are activated by reaction with ambient moisture. The hydrolysable alkoxy groups attached to the silicon end of the silane are typically either methoxy or ethoxy. Once activated (hydrolyzed), the resultant silanol groups will condense with other silanols or with reactive groups on the surface of a substrate such as SiOH, AIOH, or other metal oxides or hydroxides.The silane’s ability to bond to a surface will generally be determined by the concentration of such sites on the surface.
Selecting the optimal silane for an application requires matching the reactivity of the silane‘s organofunctional group to that of the polymer. |
 |
The silanes can be blended into an adhesive formulation or used as primers on substrates. The structure and reactivity of the silane will affect the ability of the silane to migrate. The most effective way to promote adhesion is to apply the silane as a primer to the surface, followed by application of the adhesive/sealant. In this way, the silane will be on the surface and therefore at the interface where it can enhance adhesion between the polymer and the substrate. Silane primers are usually dilute solutions of 0.5 to 5 percent silane in alcohol or water/alcohol solvent. They are wiped or sprayed on the substrate, after which the solvent is allowed to evaporate. While the concentration needed for a specific application may vary, one percent (1%) based on resin content is recommended as a good starting point. |

|
|
SiSiB® silane coupling agents are used to bind the organic polymers to a mineral or siliceous filler, increase adhesion between fillers and polymers in adhesives and sealant.
More information about Silane Coupling Agent... |
Alkoxysilanes react very rapidly with water; they are usually used to capture excess moisture in sealants and adhesives. SiSiB® PC6110, Vinyltrimethoxysilane is the most common moisture scavenger, due to the electron interactions of the vinyl group it reacts with moisture faster than other alkoxy silanes, enabling it to function as a moisture scavenger in the presence of other silanes incorporated as adhesion promoters, crosslinkers or coupling agents. The amount of silane added will depend on the water content of the formulation constituents.
|
|
 |
SiSiB® silanes can be used to crosslink polymers such as acrylates, polyethers, polyurethanes, and polyesters.
The organofunctional portion of the silane can react, and bond to, the polymer backbone in a sealant or adhesive. The alkoxysilyl group on the silane should not crosslink prematurely in order to be available to provide crosslinking once the sealant or adhesive is applied in its intended application.
More information about Silane Crosslinker...
|
|
 |
|